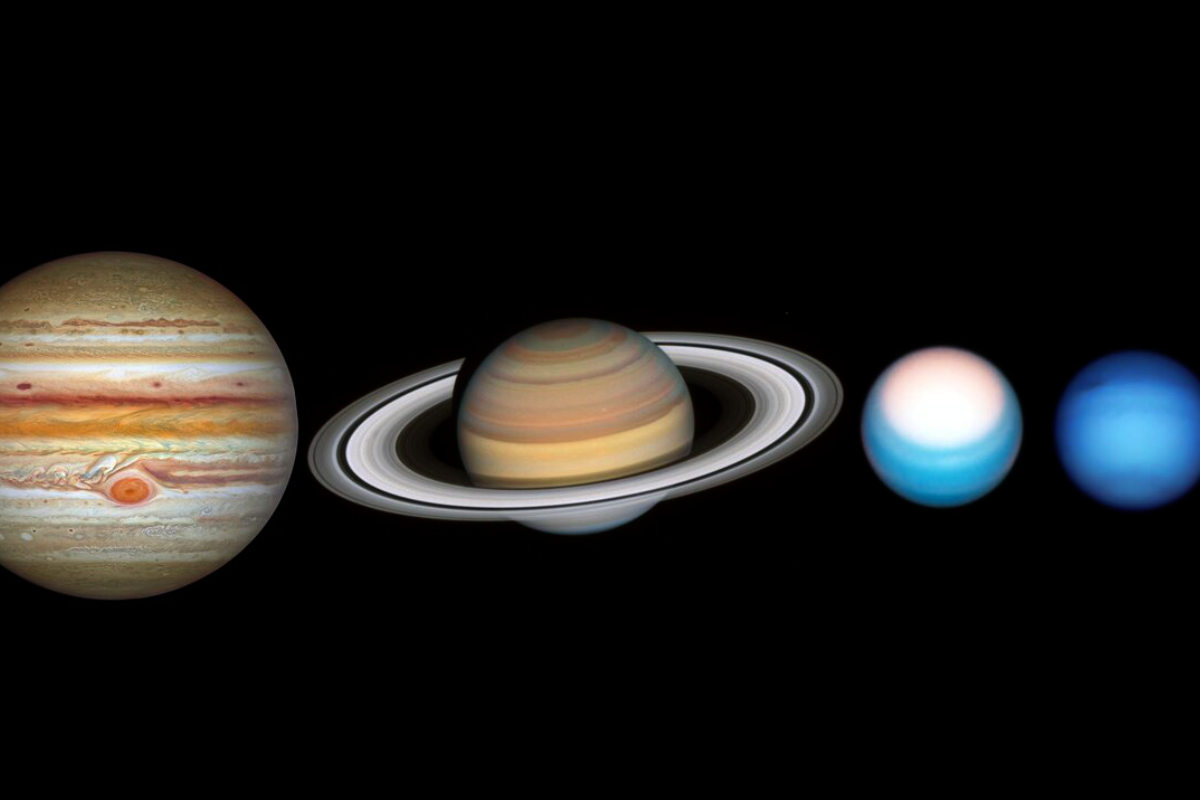
This – and more – is clear from new images taken by Hubble of the four largest planets in our solar system.
The Hubble Space Telescope makes a “round trip” every year through the outer extensions of our solar system. This is the realm of the giant planets – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune – stretching up to 30 times the distance between the Earth and the Sun. During the tour, Hubble keeps his camera ready. This again produces stunning and revealing images.
the changes
Unlike rocky planets like Earth and Mars that are close to the sun’s warmth, the planets in the outer reaches of our solar system consist of a cold, gaseous soup of hydrogen, helium, ammonia and other trace gases, packed around an intensely heated, pressurized core. This contributes to the fact that its quirky and colorful atmosphere is constantly changing. Each time Hubble points its camera at these worlds, the researchers are in for another surprise. Images often provide new insights into wild weather, driven by the largely unknown dynamics that occur beneath cloud tops.
Jupiter
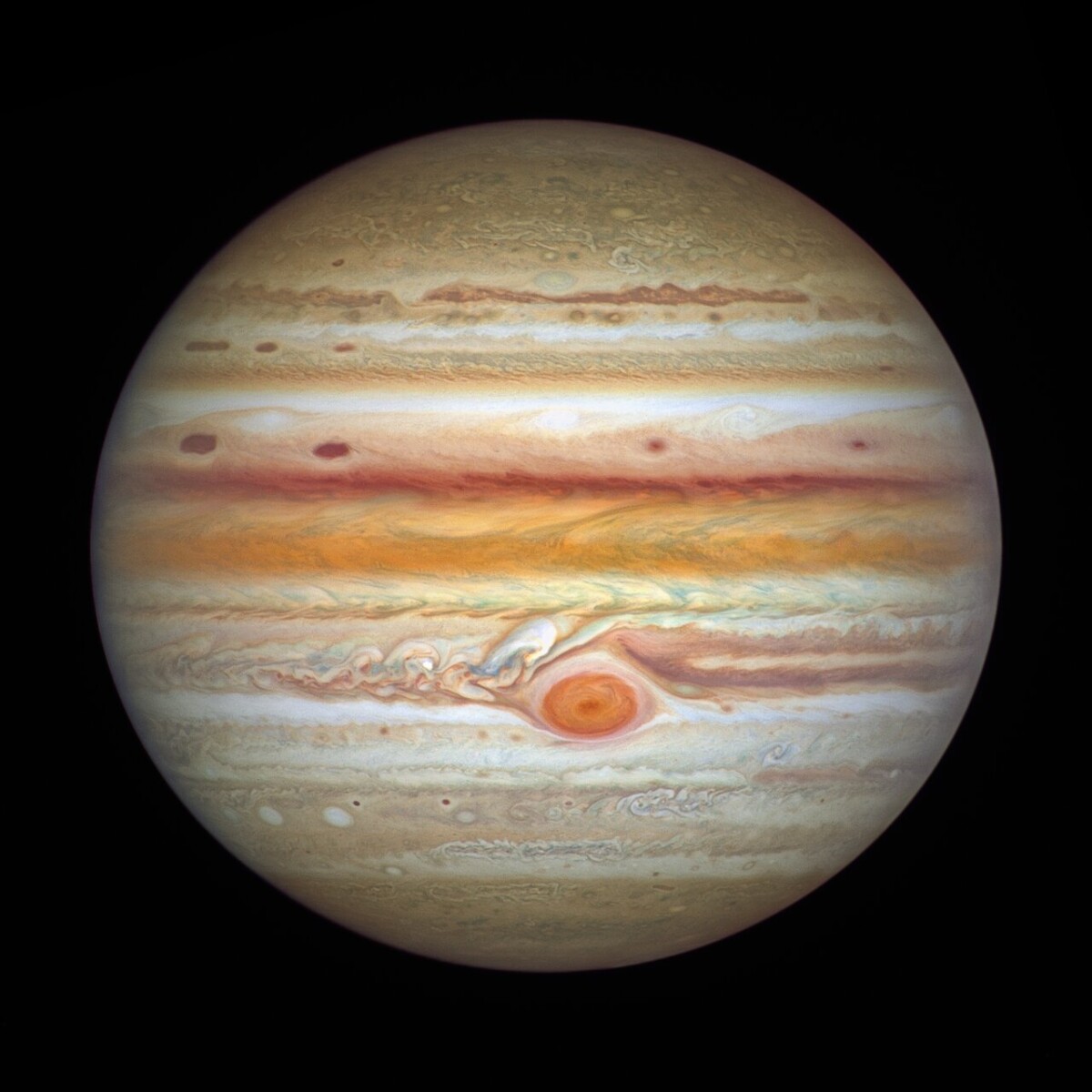
This year, it looks like Jupiter will face surprises again. Researchers have discovered that the gas giant’s equator has changed color again. The album can be admired below. You can see how the equatorial region of the planet has a deep orange tint. This is unusual. While the equator has deviated from the traditional white or beige color for a few years now, scientists are still amazed to see the equator appear true orange.
Afbeelding: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), MH Wong (University of California, Berkeley), and the Opal Team
Also of note are the many new storms that have appeared above the equator. These long storms resemble red blood cells, and are cyclonic swirls, each with a different appearance. For example, some of them are sharp and clear, while others look more blurry. This difference in appearance is due to certain physical properties in the eddies’ cloud cover.
Saturn
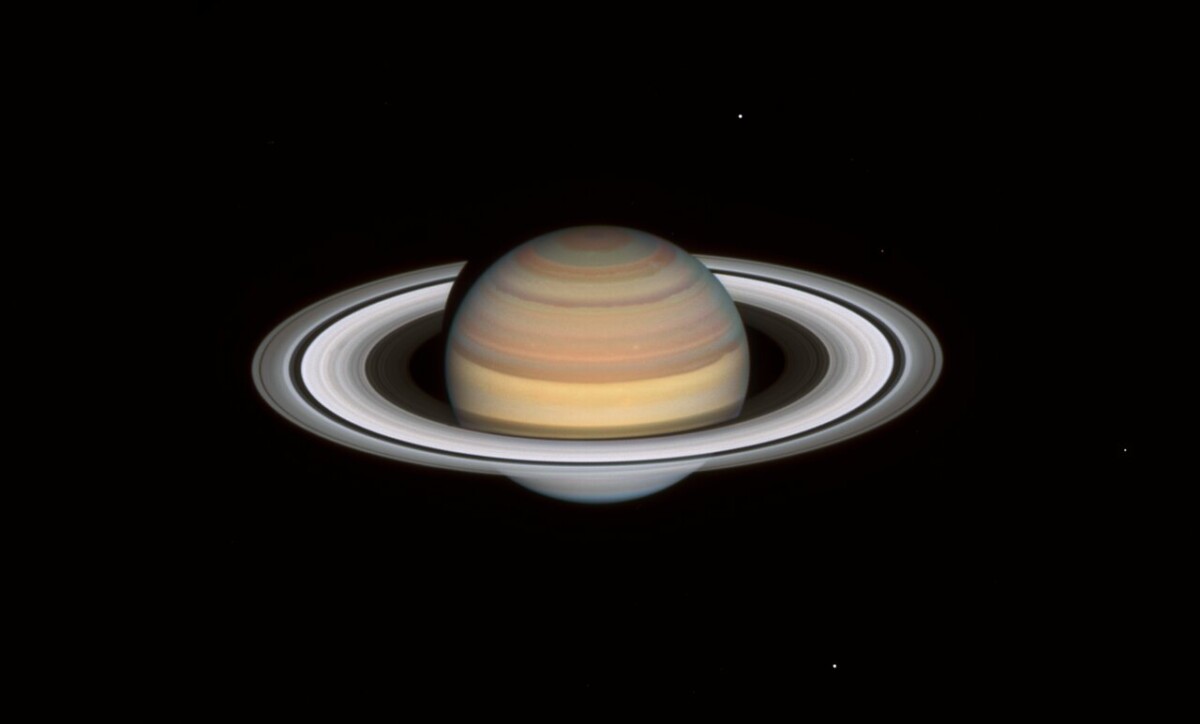
We travel to our neighbor Saturn, which has also undergone a transformation. Watch!
Afbeelding: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), MH Wong (University of California, Berkeley), and the Opal Team
The planet’s bands have changed color in the northern hemisphere – where autumn is now. It is currently winter in the Southern Hemisphere, which can be seen in the persistent bluish shade of Antarctica.
Uranus
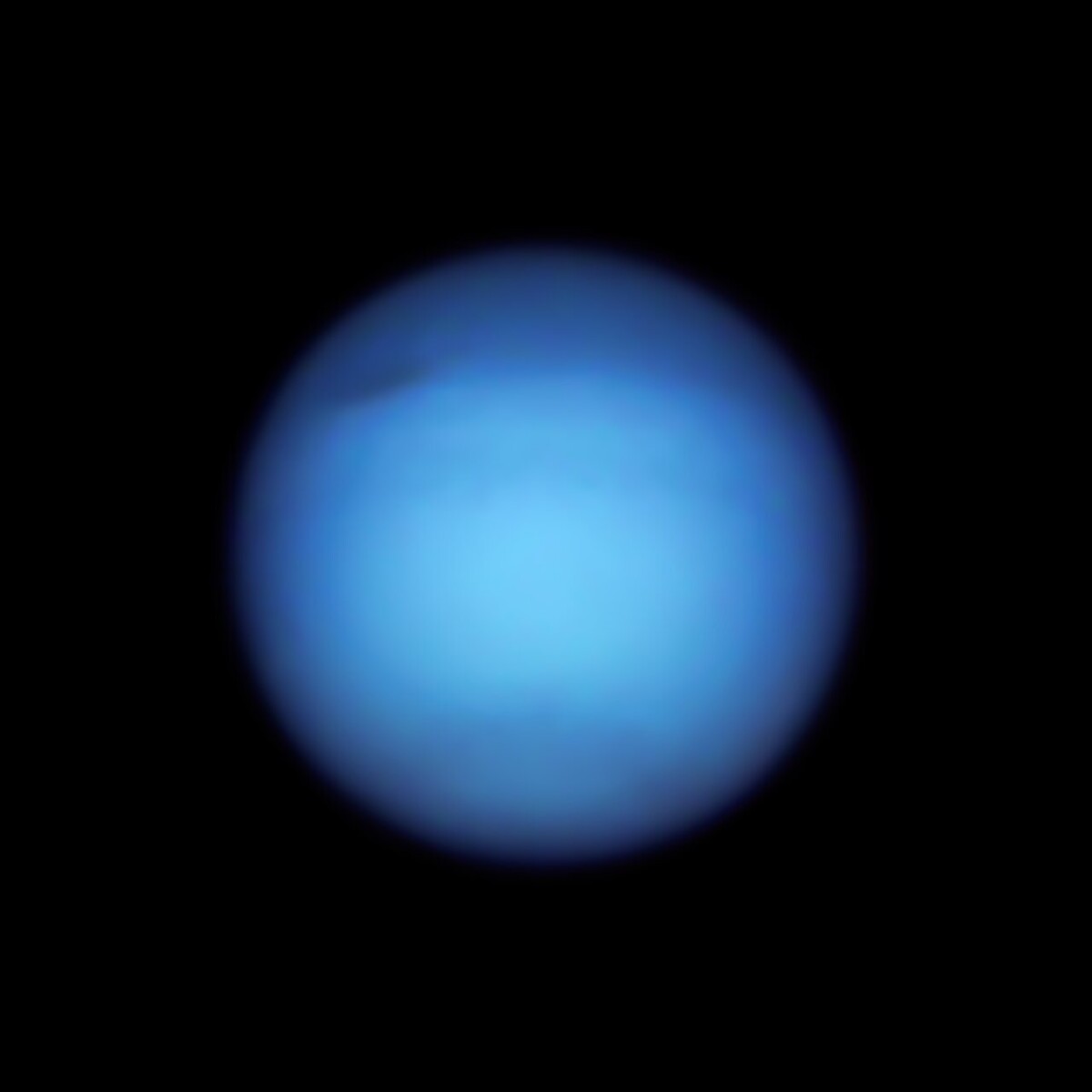
In particular, the Hubble image of Uranus highlights the planet’s bright north polar cap. It’s spring in the northern hemisphere, and the increase in ultraviolet rays from the sun appears to be making the North Pole much brighter.
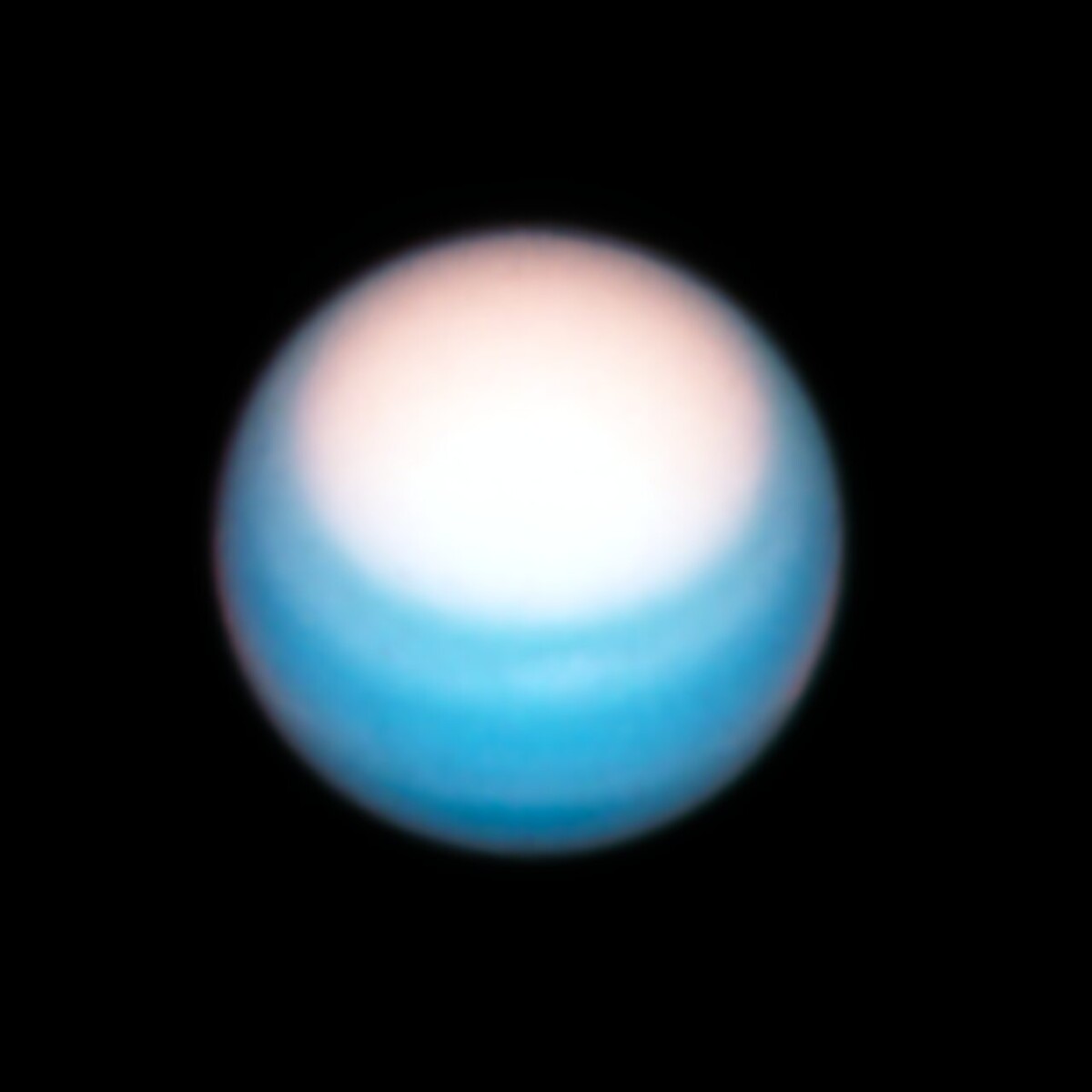

Afbeelding: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), MH Wong (University of California, Berkeley), and the Opal Team
why? The researchers owe us the answer. It may be related to a change in the opacity (light transmittance) of atmospheric methane, or a change in aerosols. However, what is noteworthy is that even when the atmospheric cover is illuminated, the sharp southern boundary remains at the same latitude. This has been the case for years. Maybe some kind of jet stream would be a tricky end?
Neptune
Finally, Hubble depicts Neptune. The photo shows the now famous “dark spot” – a massive storm Sometimes it changes direction – , along with the Northern Hemisphere. You can also spot a noticeable dark and extended circle that includes the south pole of Neptune.
Afbeelding: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), MH Wong (University of California, Berkeley), and the Opal team.
By the way, do you know where this ice giant’s blue color comes from? This coloration from Neptune and Uranus results from the absorption of red light by the methane-rich atmospheres of these two planets, combined with the same Rayleigh scattering effect that turns Earth’s clear skies blue.
Overall, the new Hubble images reveal intense and subtle changes taking place on the largest planets in our solar system. The sharp eye of a space telescope provides new insights into the fascinating and dynamic weather patterns and seasons. In addition, it allows astronomers to investigate similar and different properties that contribute to the constantly changing atmosphere.

“Lifelong zombie fanatic. Hardcore web practitioner. Thinker. Music expert. Unapologetic pop culture scholar.”